这篇教程Python统计词频并绘制图片(附完整代码)写得很实用,希望能帮到您。
效果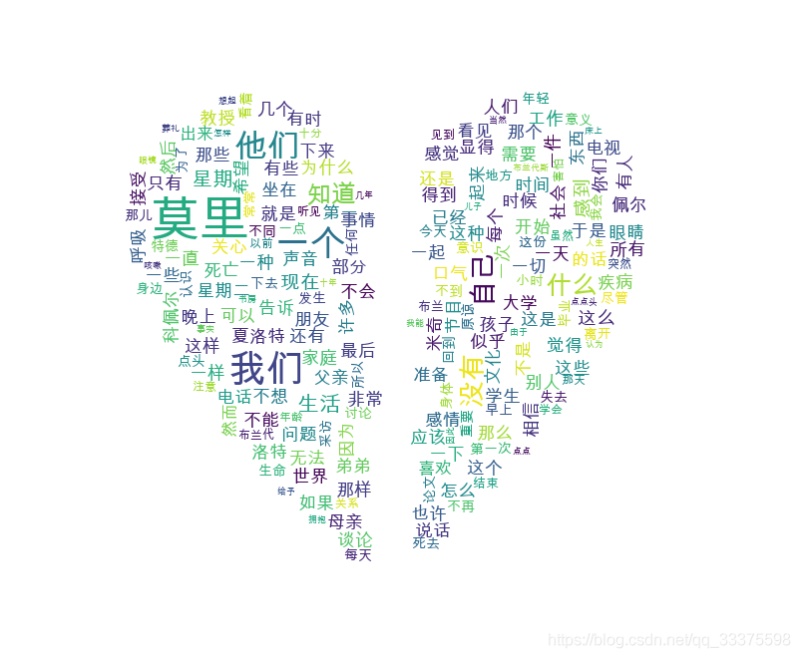
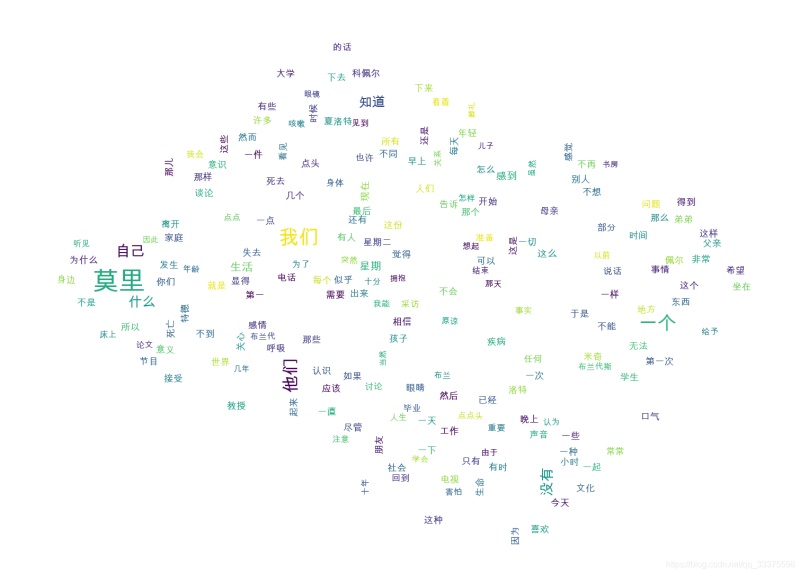


1 实现代码读取txt文件: def readText(text_file_path): with open(text_file_path, encoding='gbk') as f: # content = f.read() return content 得到文章的词频: def getRecommondArticleKeyword(text_content, key_word_need_num = 10, custom_words = [], stop_words =[], query_pattern = 'searchEngine'): ''' :param text_content: 文本字符串 :param key_word_need_num: 需要的关键词数量 :param custom_words: 自定义关键词 :param stop_words: 不查询关键词 :param query_pattern: precision:精确模式————试图将句子最精确地切开,适合文本分析; entire:全模式————把句子中所有的可以成词的词语都扫描出来, 速度非常快,但是不能解决歧义; searchEngine:搜索引擎模式————在精确模式的基础上,对长词再次切分,提高召回率,适合用于搜索引擎分词; paddle模式————利用PaddlePaddle深度学习框架,训练序列标注(双向GRU)网络模型实现分词。同时支持词性标注。 :return: ''' # jieba.enable_paddle() # paddle.fluid.install_check.run_check() if not isinstance(text_content, str): raise ValueError('文本字符串类型错误!') if not isinstance(key_word_need_num, int): raise ValueError('关键词个数类型错误!') if not isinstance(custom_words, list): raise ValueError('自定义关键词类型错误!') if not isinstance(stop_words, list): raise ValueError('屏蔽关键词类型错误!') if not isinstance(query_pattern, str): raise ValueError('查询模式类型错误!') # 添加自定义关键词 for word in custom_words: jieba.add_word(word) if query_pattern == 'searchEngine': key_words = jieba.cut_for_search(text_content) elif query_pattern == 'entire': key_words = jieba.cut(text_content, cut_all=True, use_paddle=True) elif query_pattern == 'precision': key_words = jieba.cut(text_content, cut_all=False, use_paddle=True) else: return [] # print("拆分后的词: %s" % " ".join(key_words)) # 过滤后的关键词 stop_words = set(stop_words) word_count = Counter() for word in key_words: if len(word) > 1 and word not in stop_words: word_count[word] += 1 # res_words = list() # for data in word_count.most_common(key_word_need_num): # res_words.append(data[0]) # return res_words return word_count绘制图片: def drawWordsCloud(word_count, save_img_filePath='', img_mask_filePath=''): # print(word_count) # print(type(word_count)) if len(img_mask_filePath) != 0: img_mask = np.array(Image.open(img_mask_filePath)) #打开遮罩图片,将图片转换为数组 wc = wordcloud.WordCloud(font_path='/Library/Fonts/Arial Unicode.ttf',# 设置中文字体,词云默认字体是“DroidSansMono.ttf字体库”,不支持中文 background_color="white", # 设置背景颜色 max_words=200, # 设置最大显示的字数 max_font_size=50, # 设置字体最大值 random_state=30, # 设置有多少种随机生成状态,即有多少种配色方案 width=400, height=200, mask=img_mask ) else: wc = wordcloud.WordCloud(font_path='/Library/Fonts/Arial Unicode.ttf',# 设置中文字体,词云默认字体是“DroidSansMono.ttf字体库”,不支持中文 background_color="white", # 设置背景颜色 max_words=200, # 设置最大显示的字数 max_font_size=50, # 设置字体最大值 random_state=30, # 设置有多少种随机生成状态,即有多少种配色方案 width=400, height=200 ) # 绘图 wc.generate_from_frequencies(word_count) #从字典生成词云 plt.imshow(wc) #显示词云 plt.axis('off') #关闭坐标轴 plt.show() #显示图像 # 保存图片 if len(save_img_filePath) != 0: wc.to_file(save_img_filePath) else: pass2 完整代码#-*- coding : utf-8-*-import jiebafrom collections import Counterimport paddleimport wordcloud #词云展示库import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #图像展示库import timefrom PIL import Imageimport numpy as npdef timer(func): def calculateTime(*args, **kwargs): t = time.perf_counter() result = func(*args, **kwargs) print(f'func {func.__name__} coast time:{time.perf_counter() - t:.8f} s') return result return calculateTimedef readText(text_file_path): with open(text_file_path, encoding='gbk') as f: # content = f.read() return content@timerdef getRecommondArticleKeyword(text_content, key_word_need_num = 10, custom_words = [], stop_words =[], query_pattern = 'searchEngine'): ''' :param text_content: 文本字符串 :param key_word_need_num: 需要的关键词数量 :param custom_words: 自定义关键词 :param stop_words: 不查询关键词 :param query_pattern: precision:精确模式————试图将句子最精确地切开,适合文本分析; entire:全模式————把句子中所有的可以成词的词语都扫描出来, 速度非常快,但是不能解决歧义; searchEngine:搜索引擎模式————在精确模式的基础上,对长词再次切分,提高召回率,适合用于搜索引擎分词; paddle模式————利用PaddlePaddle深度学习框架,训练序列标注(双向GRU)网络模型实现分词。同时支持词性标注。 :return: ''' # jieba.enable_paddle() # paddle.fluid.install_check.run_check() if not isinstance(text_content, str): raise ValueError('文本字符串类型错误!') if not isinstance(key_word_need_num, int): raise ValueError('关键词个数类型错误!') if not isinstance(custom_words, list): raise ValueError('自定义关键词类型错误!') if not isinstance(stop_words, list): raise ValueError('屏蔽关键词类型错误!') if not isinstance(query_pattern, str): raise ValueError('查询模式类型错误!') # 添加自定义关键词 for word in custom_words: jieba.add_word(word) if query_pattern == 'searchEngine': key_words = jieba.cut_for_search(text_content) elif query_pattern == 'entire': key_words = jieba.cut(text_content, cut_all=True, use_paddle=True) elif query_pattern == 'precision': key_words = jieba.cut(text_content, cut_all=False, use_paddle=True) else: return [] # print("拆分后的词: %s" % " ".join(key_words)) # 过滤后的关键词 stop_words = set(stop_words) word_count = Counter() for word in key_words: if len(word) > 1 and word not in stop_words: word_count[word] += 1 # res_words = list() # for data in word_count.most_common(key_word_need_num): # res_words.append(data[0]) # return res_words return word_countdef drawWordsCloud(word_count, save_img_filePath='', img_mask_filePath=''): # print(word_count) # print(type(word_count)) if len(img_mask_filePath) != 0: img_mask = np.array(Image.open(img_mask_filePath)) #打开遮罩图片,将图片转换为数组 wc = wordcloud.WordCloud(font_path='/Library/Fonts/Arial Unicode.ttf',# 设置中文字体,词云默认字体是“DroidSansMono.ttf字体库”,不支持中文 background_color="white", # 设置背景颜色 max_words=200, # 设置最大显示的字数 max_font_size=50, # 设置字体最大值 random_state=30, # 设置有多少种随机生成状态,即有多少种配色方案 width=400, height=200, mask=img_mask ) else: wc = wordcloud.WordCloud(font_path='/Library/Fonts/Arial Unicode.ttf',# 设置中文字体,词云默认字体是“DroidSansMono.ttf字体库”,不支持中文 background_color="white", # 设置背景颜色 max_words=200, # 设置最大显示的字数 max_font_size=50, # 设置字体最大值 random_state=30, # 设置有多少种随机生成状态,即有多少种配色方案 width=400, height=200 ) # 绘图 wc.generate_from_frequencies(word_count) #从字典生成词云 plt.imshow(wc) #显示词云 plt.axis('off') #关闭坐标轴 plt.show() #显示图像 # 保存图片 if len(save_img_filePath) != 0: wc.to_file(save_img_filePath) else: passif __name__ == '__main__': pass # /Users/mac/Downloads/work/retailSoftware/公司项目/test.txt text_file_path = "/Users/mac/Downloads/电子书/编程思想/相约星期二/相约星期二.txt" # text_file_path = "/Users/mac/Downloads/work/retailSoftware/公司项目/test3.txt" text_content = readText(text_file_path) # print(text_content) # print(JNI_API_getRecommondArticleKeyword(text_content)) img_mask_filePath = '/Users/mac/Desktop/截屏2021-08-20 下午4.02.10.png' img_save_filePath = '/Users/mac/Downloads/test9.png' drawWordsCloud(getRecommondArticleKeyword(text_content), img_save_filePath, img_mask_filePath)到此这篇关于Python统计词频并绘制图片(附完整代码)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python统计词频绘制图片内容请搜索51zixue.net以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持51zixue.net!
一篇文章带你了解python正则表达式的正确用法
零基础学习Python爬虫 |

