这篇教程python最短路径的求解Dijkstra算法示例代码写得很实用,希望能帮到您。
前言书接上回,之前的博客使用图论求解最短路径,但是只使用了 Matlab 的shortestpath 函数和 python 的 nx.shortest_path 函数进行求解。本文再介绍一种算法求解最短路径。
一、Dijkstra算法(迪克斯特拉算法)- Dijkstra算法是一种广泛使用的单源最短路径算法,它能够找到一个加权图中从一个起始节点到其他所有节点的最短路径。这个算法最适合于边的权重都是非负值的图。
算法步骤以下是Dijkstra算法的详细步骤: 1.初始化:将源节点到自身的距离设为0,其他节点的距离设为无穷大。将所有节点标记为未访问。 2.选择未访问节点中距离最小的节点:将其标记为已访问,如果所有未访问节点的距离都是无穷大,
算法终止。 3.更新邻居节点的距离:对于邻居节点,如果通过当前节点可以获得更短的路径,则更新其距离。 4.重复步骤2和3,直到所有节点都被访问过或者目标节点的最短路径已经确定。
堆 heapq- Dijkstra算法求解最短路径问题时,需要选择未访问节点中距离最小的节点。而堆可以用于高效地找到具有最小距离的节点。
heapq 是 Python 标准库中的一个模块,提供了堆队列算法的实现,也称为优先队列算法。堆是一种特殊的树状数据结构,可以高效地支持插入和最小值/最大值的提取操作。Python 中的 heapq 实现了最小堆,即堆顶元素是最小值。
基本功能下面是 heapq 中的一些基本函数及其解释: heapq.heappush(heap, item): 将元素 item 添加到堆中,保持堆的不变性。heapq.heappop(heap): 弹出并返回堆中的最小元素,同时保持堆的不变性。如果堆为空,会引发 IndexError。heapq.heappushpop(heap, item): 将元素 item 添加到堆中,然后弹出并返回堆中的最小元素。这个操作是原子的,效率比分开执行 heappush 和 heappop 更高。heapq.heapify(iterable): 将可迭代对象转换为堆。heapq.nlargest(n, iterable, key=None): 返回可迭代对象中最大的 n 个元素。heapq.nsmallest(n, iterable, key=None): 返回可迭代对象中最小的 n 个元素。
重点强调两个函数: heapq.heappush(heap, item): 将元素 item 添加到堆中,函数返回值是添加元素 item后的值(既包含原来的元素,也包含元素 item 。
heapq.heappop(heap): 弹出并返回堆中的最小元素,同时保持堆的不变性。函数返回值是堆中的最小元素,并且堆更新为不含有最小元素。
二、示例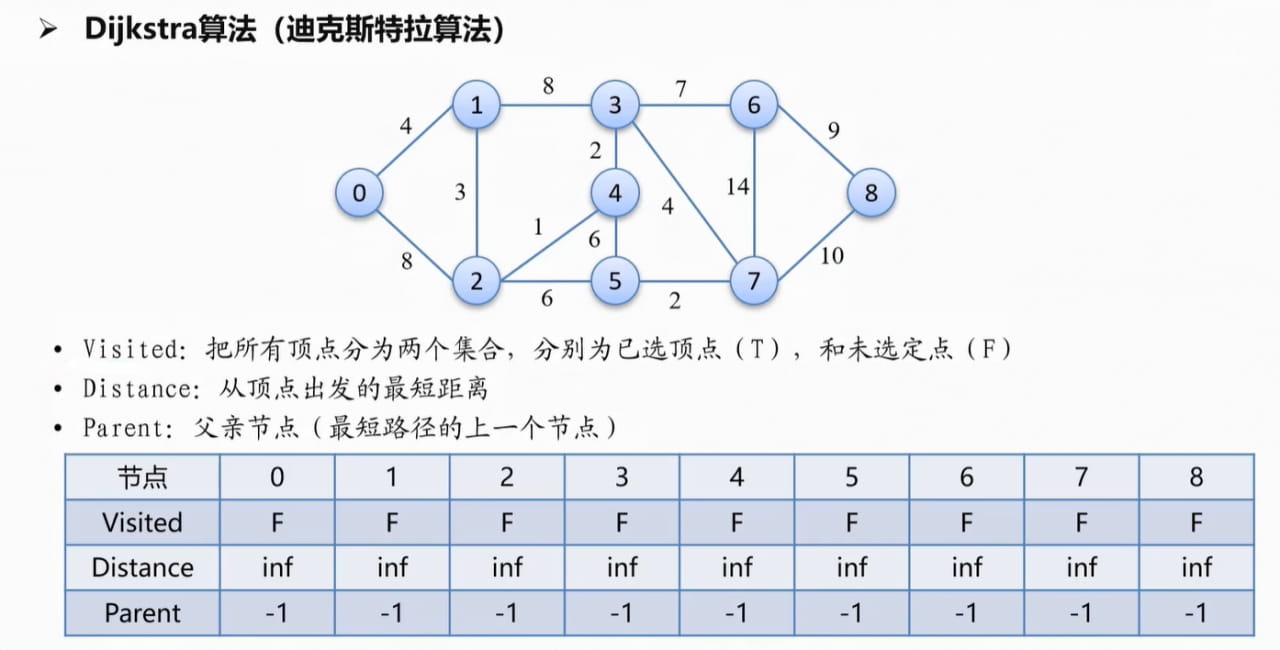
表示出示例图# 示例图(邻接表表示)graph = { '0': {'1': 4, '2': 8}, '1': {'0': 4, '2': 3, '3': 8}, '2': {'0': 8, '1': 3, '4': 1, '5': 6}, '3': {'1': 8, '4': 2, '6': 7, '7': 4}, '4': {'2': 1, '3': 2, '5': 6}, '5': {'2': 6, '4': 6, '7': 2}, '6': {'3': 7, '7': 14, '8': 9}, '7': {'3': 4, '5': 2, '6': 14, '8': 10}, '8': {'6': 9, '7': 10}}
定义Dijkstra算法函数- 源节点到自身的距离设为0,其他节点的距离设为无穷大
# 初始化距离字典,将所有节点的距离设为无穷大distances = {vertex: float('infinity') for vertex in graph}distances[start] = 0- 初始化父亲节点(由于此时未访问任何节点所以全部设置为
None )
# 初始化父亲节点parent = {vertex: None for vertex in graph}# 初始化优先队列,并将起始节点入队priority_queue = [(0, start)] (1)取出当前访问节点中距离最小的节点 (2)更新该节点相邻的节点和距离 (3)比较节点间的距离,若有更短的路径,则更新距离和该节点的父亲节点,并将该节点加入待比较的节点 while priority_queue: # 弹出堆中距离最小的节点 current_distance, current_vertex = heapq.heappop(priority_queue) # print("距离最小的节点是:",current_distance, current_vertex, "更新后的队列:",priority_queue) # 如果当前距离已经大于已知的最短距离,则跳过 if current_distance > distances[current_vertex]: continue # 更新相邻节点的距离 for neighbor, weight in graph[current_vertex].items(): distance = current_distance + weight # print("相邻节点的距离:",neighbor,distance) # 如果找到更短的路径,则更新距离,并将节点加入优先队列 if distance < distances[neighbor]: distances[neighbor] = distance parent[neighbor] = current_vertex heapq.heappush(priority_queue, (distance, neighbor)) # print("加入后的队列:",priority_queue)当访问到最后一个节点时,heapq.heappop(heap) 函数弹出堆中最小的元素,堆中元素为空,退出循环。 Dijkstra算法函数代码 def dijkstra(graph,start): distances = {vertex: float('infinity') for vertex in graph} distances[start] = 0 # 初始化父亲节点 parent = {vertex: None for vertex in graph} priority_queue = [(0,start)] while priority_queue: # 弹出堆中距离最小的节点 current_distance, current_vertex = heapq.heappop(priority_queue) # print("距离最小的节点是:",current_distance, current_vertex, "更新后的队列:",priority_queue) # 如果当前距离已经大于已知的最短距离,则跳过 if current_distance > distances[current_vertex]: continue # 更新相邻节点的距离 for neighbor, weight in graph[current_vertex].items(): distance = current_distance + weight # print("相邻节点的距离:",neighbor,distance) # 如果找到更短的路径,则更新距离,并将节点加入优先队列 if distance < distances[neighbor]: distances[neighbor] = distance parent[neighbor] = current_vertex heapq.heappush(priority_queue, (distance, neighbor)) # print("加入后的队列:",priority_queue) return distances, parent函数返回值:从起始点到每个节点的最短距离,和每个节点对应的父亲节点。
根据父亲节点,回溯最短路径访问所有节点后得到的结果: 
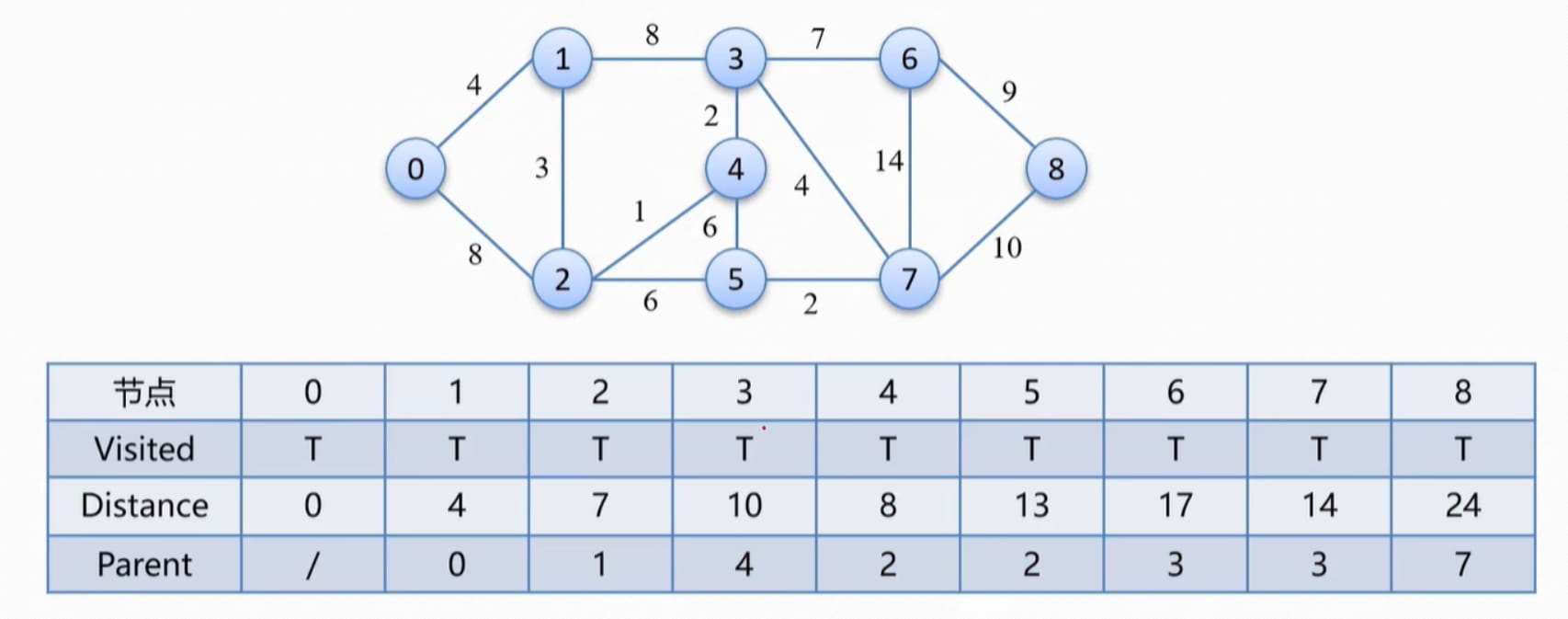
要求从 0 到 8 的最短距离,就从 8 开始回溯,8 的父亲节点是 7 ,7 的父亲节点是 3 ,3 的父亲节点是 4 ,4 的父亲节点是 2 ,2 的父亲节点是 1 ,1 的父亲节点是 0 ;所以从 0 到 8 的最短路径为: 0 —> 1 —> 2 —> 4 —> 3 —> 7 —> 8 代码如下: # 输出路径回溯def get_path(parent, start, end): path = [] current = end while current is not None: path.append(current) current = parent[current] path.reverse() return path
三、python 代码import heapqgraph = { '0': {'1': 4, '2': 8}, '1': {'0': 4, '2': 3, '3': 8}, '2': {'0': 8, '1': 3, '4': 1, '5': 6}, '3': {'1': 8, '4': 2, '6': 7, '7': 4}, '4': {'2': 1, '3': 2, '5': 6}, '5': {'2': 6, '4': 6, '7': 2}, '6': {'3': 7, '7': 14, '8': 9}, '7': {'3': 4, '5': 2, '6': 14, '8': 10}, '8': {'6': 9, '7': 10}}def dijkstra(graph,start): distances = {vertex: float('infinity') for vertex in graph} distances[start] = 0 # 初始化父亲节点 parent = {vertex: None for vertex in graph} priority_queue = [(0,start)] while priority_queue: # 弹出堆中距离最小的节点 current_distance, current_vertex = heapq.heappop(priority_queue) # print("距离最小的节点是:",current_distance, current_vertex, "更新后的队列:",priority_queue) # 如果当前距离已经大于已知的最短距离,则跳过 if current_distance > distances[current_vertex]: continue # 更新相邻节点的距离 for neighbor, weight in graph[current_vertex].items(): distance = current_distance + weight # print("相邻节点的距离:",neighbor,distance) # 如果找到更短的路径,则更新距离,并将节点加入优先队列 if distance < distances[neighbor]: distances[neighbor] = distance parent[neighbor] = current_vertex heapq.heappush(priority_queue, (distance, neighbor)) # print("加入后的队列:",priority_queue) return distances, parentdistances, parent = dijkstra(graph, '0')# print(parent)# print(distances)# 输出路径回溯def get_path(parent, start, end): path = [] current = end while current is not None: path.append(current) current = parent[current] path.reverse() return pathend_node = '8'path = get_path(parent, '0', end_node)print(f"从节点 '0' 到节点 {end_node} 的路径:", path)运行结果: 
总结本文说明了如何使用Dijkstra算法求解最短路径的问题,并使用python进行了代码编写。 到此这篇关于python最短路径的求解Dijkstra算法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python最短路径求解Dijkstra算法内容请搜索本站以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持本站!
Python使用Dask进行大规模数据处理
Python |

