这篇教程python使用tkinter包实现进度条写得很实用,希望能帮到您。
python中的tkinter包是一种常见的设计程序的GUI界面用的包。本文主要介绍这里面的一个组件:进度条(Progressbar)。Tkinter Progressbar里面对进度条组件已经做了一定的介绍,但比较抽象。本文以另一种方式介绍这个组件及其常用用法。
一、进度条的基本概念进度条组件涉及多个基本概念,但本文主要介绍几个最重要的概念。而至于其它概念,多半只是涉及一些细节优化。
(一)进度条模式tkinter支持两种模式的进度条: 1. determinate模式 这种模式的进度条通常是这样的: 
也就是说,这样的进度条适用于任务的完成进度明确,且可以量化的情况。 2. indeterminate模式 这种模式的进度条通常是这样的: 
也就是说,这样的进度条适用于任务的完成进度不明确或无法量化的情况。进度条的滚动只能表示任务正在运行中,无法表示任务完成了多少。
(二)进度条绑定的变量进度条组件通常要绑定一个数值型变量,如Int或Double,这个变量存放进度条的进度数值。 对于determinate模式下的进度条,数值通常从0开始,随着进度的发展不断升高(如何升高将在下一节进行说明),但到达99后,继续升高将清零,重新从0开始。也就是说,如果进度量是x,那么该数值变量的值是x%100。(%表示取余)但数值可以手动调为100,此时进度条满格。 对于indeterminate模式下的进度条,数值通常从0开始,随着进度的发展不断升高,没有止境。 以上是对基本概念的介绍。下面贴上进度条组件相关的代码进行进一步说明。 prgVar = DoubleVar(value=0)prgb = ttk.Progressbar(root, orient='horizontal', length=200, mode='determinate', variable=prgVar)prgb.grid(row=0, columnspan=4) 在对象prgb里,variable参数对应的变量是prgVar,所以prgVar是进度条组件prgb绑定的变量。这个组件的模式是determinate。 用一个标签组件(Label)显示该变量的数值。 labl = Label(root, textvariable=prgVar)labl.grid(row=2, columnspan=4) 效果如下: 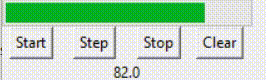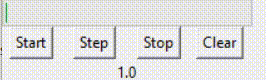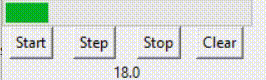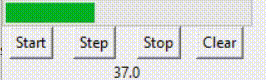
如动画中所示,变量值到达99后退回了0,重新开始。 但如果是indeterminate模式,则是另一种情况。 prgbInfVar = IntVar(value=0)prgbInf = ttk.Progressbar(root, orient="horizontal", length=200, mode='indeterminate', variable=prgbInfVar)prgbInf.grid(row=3, columnspan=4)lablInf = Label(root, textvariable=prgbInfVar)lablInf.grid(row=5, columnspan=4) 效果如下: 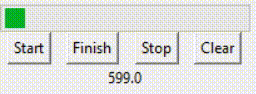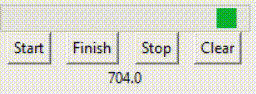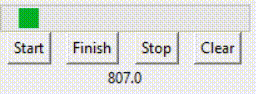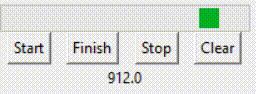
如动画中所示,变量值一直在不断增加。
(三)进度条的动作前面所示的那些动画中,进度条都是以一个速度在递进,数值也在增加。当然,进度条的数值可以通过人工调整其对应变量的值来设置,进度条的显示也会随数值而变化。 例如,要把determinate的进度条清空,只需将进度条绑定的变量值设为0即可。 此时进度条变空。 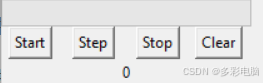
于此同时,进度条有start,step,以及stop三个常用动作。 prgb.start(p)prgb.step(x)prgb.stop() 以上三行代码,分别表示: 1. 进度条prgb开始自动递增,每隔p毫秒递增1。 2. 进度条prgb一次性递增x。该动作和进度条当前是否在自动递增无关,执行后也不会影响进度条是否继续自动递增。 3. 进度条prgb停止自动递增。注意该动作并不自动将进度条清零。 注意:若进度条的模式是determinate,以上动作执行时仍然遵守进度条变量超过99清零的规则。
二、程序示例现在用一个例子来帮助读者复习进度条的相关知识。 有很多人在设计程序时,希望实现这样的显示: 当任务尚未开始时,进度条应为空 
当任务正在进行时,由于任务的进度无法确认或量化,只能用indeterminate模式的进度条表示 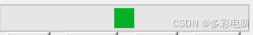
当任务失败时,进度条回到空的状态。但当任务完成时,进度条应为满 
这样的逻辑如何实现呢?对于indeterminate模式下的进度条,无论绑定的变量值为多少,都不可能实现进度条为空或满的显示。 此时,就需要将进度条的模式转变为determinate prgbInf['mode'] = 'determinate' 在这里设计一个程序,实现这样的逻辑: 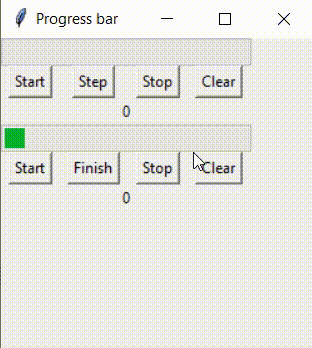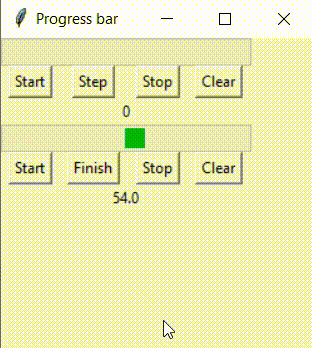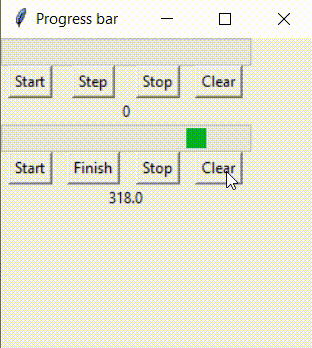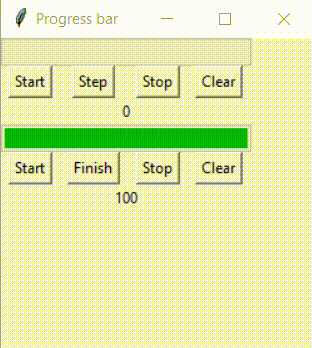
完整的代码: from tkinter import *from tkinter import ttk root = Tk()root.geometry('250x250')root.title('Progress bar') def startProgress(): prgb.start(100) #increment 1 per 100ms #labl['text'] = prgb['value']def stepProgress(): prgb.step(20) #increment 20 #labl['text'] = prgb['value']def stopProgress(): prgb.stop() #labl['text'] = prgb['value']def clearProgress(): prgVar.set(0) def startProgressInf(): prgbInf['mode'] = 'indeterminate' prgbInf.start(30) #increment 1 per 100ms #labl['text'] = prgb['value']def finishProgressInf(): prgbInfVar.set(100) prgbInf.stop() prgbInf['mode'] = 'determinate' #labl['text'] = prgb['value']def stopProgressInf(): prgbInf['mode'] = 'indeterminate' prgbInf.stop() #labl['text'] = prgb['value']def clearProgressInf(): prgbInfVar.set(0) prgbInf.stop() prgbInf['mode'] = 'determinate' prgVar = DoubleVar(value=0)prgb = ttk.Progressbar(root, orient='horizontal', length=200, mode='determinate', variable=prgVar) #If progress bar has determined progress value, then use thisprgb.grid(row=0, columnspan=4) btStart = Button(root, text="Start", command=startProgress)btStart.grid(row=1, column=0)btStep = Button(root, text="Step", command=stepProgress)btStep.grid(row=1, column=1)btStop = Button(root, text="Stop", command=stopProgress)btStop.grid(row=1, column=2)btClear = Button(root, text="Clear", command=clearProgress)btClear.grid(row=1, column=3) labl = Label(root, textvariable=prgVar)labl.grid(row=2, columnspan=4) prgbInfVar = IntVar(value=0)prgbInf = ttk.Progressbar(root, orient="horizontal", length=200, mode='indeterminate', variable=prgbInfVar)prgbInf.grid(row=3, columnspan=4) btStartInf = Button(root, text="Start", command=startProgressInf)btStartInf.grid(row=4, column=0)btFinishInf = Button(root, text="Finish", command=finishProgressInf)btFinishInf.grid(row=4, column=1)btStopInf = Button(root, text="Stop", command=stopProgressInf)btStopInf.grid(row=4, column=2)btClearInf = Button(root, text="Clear", command=clearProgressInf)btClearInf.grid(row=4, column=3) lablInf = Label(root, textvariable=prgbInfVar)lablInf.grid(row=5, columnspan=4) #So, firstly, start, stop, step works for both determinate progress bar and indeterminate progress bar#secondly, for determinate progress bar the value loops from 0 to 100, reset when full#but for indeterminate progress bar, the value keeps increasing. root.mainloop()在这个程序里,btStartInf按钮实现了任务正在进行时的进度条,btClearInf按钮实现了任务失败的进度条,btFinishInf按钮实现了任务完成的进度条。具体实现方式,见按钮对应的函数。 到此这篇关于python使用tkinter包实现进度条的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python tkinter进度条内容请搜索本站以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持本站!
Python实现缓存的两个简单方法
使用Python自动备份重要文件 |

