| 需要引入的头文件:
1.打开文件打开一个已存在的文件 int open(const char *pathname, int flags); 新建一个文件并创建权限 int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
参数介绍pathname:将要打开的文件路径和名称 flags:打开标志 标志介绍: The argument flags must include one of the following access modes:O_RDONLY, O_WRONLY, or O_RDWR. These request opening the file read-only, write-only, or read/write, respectively. O_RDONLY 只读打开 O_RDWR 读写打开 O_CREAT 文件不存在则创建 O_APPEND 文件末尾追加 O_TRUNC 清空文件,重新写入 mode The following symbolic constants are provided for mode:S_IRWXU 00700 user (file owner) has read, write, and execute permission S_IRUSR 00400 user has read permissionS_IWUSR 00200 user has write permissionS_IXUSR 00100 user has execute permissionS_IRWXG 00070 group has read, write, and execute permissionS_IRGRP 00040 group has read permissionS_IWGRP 00020 group has write permissionS_IXGRP 00010 group has execute permissionS_IRWXO 00007 others have read, write, and execute permissionS_IROTH 00004 others have read permissionS_IWOTH 00002 others have write permissionS_IXOTH 00001 others have execute permission 返回值:文件描述符
2. 读文件ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count); 参数介绍 fd:对应打开的文件描述符buf : 存放数据的空间count: 计划一次从文件中读多少字节数据返回值: 实际读到的字节数
3. 写文件ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count); 参数介绍: fd :对应打开的文件描述符buf:存放待写入的数据count:计划一次向文件中写入多少数据
4.关闭fd :对应的文件描述符
分析题如果父进程先打开一个文件,fork 后子进程是否可以共享使用? 文件内容 
代码 #include<stdio.h>#include<unistd.h>#include<assert.h>#include<fcntl.h>#include<stdlib.h>int main(){ char buff[128] = {0}; int fd = open("myfile.txt", O_RDONLY); pid_t pid = fork(); assert(pid != -1); if (pid == 0) { read(fd, buff, 1); printf("child buff = %s/n", buff); sleep(1); read(fd, buff, 1); printf("child buff = %s/n", buff); } else { read(fd, buff, 1); printf("parent buff = %s/n", buff); sleep(1); read(fd, buff, 1); printf("parent buff = %s/n", buff); } close(fd); exit(0);}运行结果: 
结论: 由于 fork 创建的子进程的 PCB 是拷贝父进程的,子进程的 PCB 中的文件表指向打开文件的指针只是拷贝了父进程 PCB 中的值,所以父子进程共享父进程 fork 之前打开的所有文件描述符。 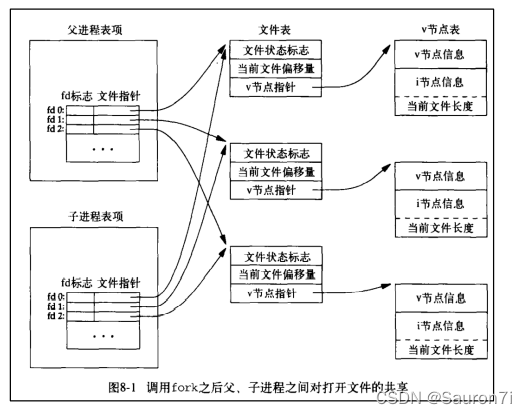
练习题完成对一个文件的复制(类似命令:cp) 原文件内容为: 
代码: #include<stdio.h>#include<unistd.h>#include<fcntl.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<assert.h>int main(void){ char buff[128] = {0}; int fdr = open("myfile.txt", O_RDONLY); assert(fdr != -1); int fdw = open("newfile.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0600); assert(fdw != -1); int n = 0; while (n = read(fdr, buff, 128) > 0) { write(fdw, buff, n); } close(fdr); close(fdw); exit(0);}运行示例: 可以看到newfile.txt创建成功 
系统调用和库函数的区别区别: 系统调用的实现在内核中,属于内核空间,库函数的实现在函数库中,属于用户空间。 系统调用执行过程: 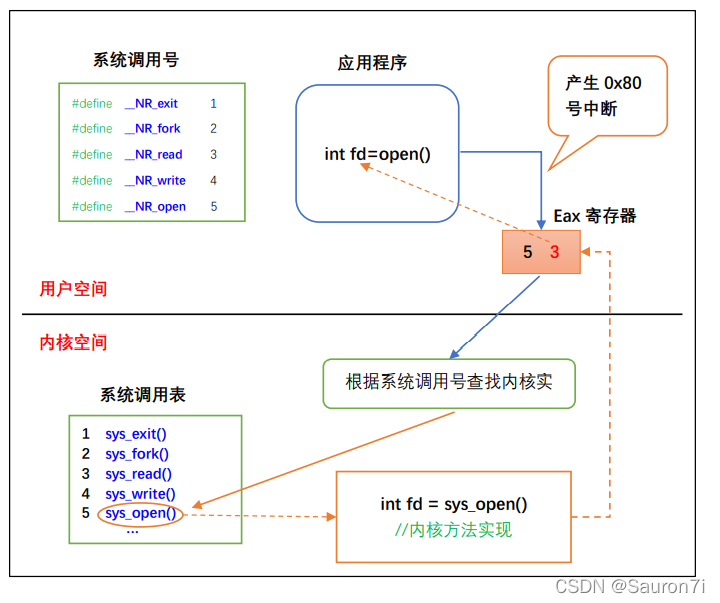
下载地址:
linux缩减XFS分区格式的根目录
Linux内存管理和寻址详细介绍 |

